————————————————————————————————
Monthly Discussion
Is the NYSE
Overvalued or Undervalued at Present?
This month's
discussion updates the bubble indicator as described in An S-Shaped Trail to Wall Street
(pp 75-79).
The approach in
brief
Using the notion
of relative price one can objectively understand whether the market is
overvalued or undervalued and estimate how close we may be to bursting a bubble
or to bottoming out from a major dip.
The DJIA that we study and forecast in this Newsletter is calculated from
the average DOW price weighted by the share volume. This price is calculated as
the ratio of the DJIA’s dollar value over the DJIA’s share volume and is
expressed in dollars. The same ratio, but with dollar value and share volume
expressed as percentages of the NYSE totals, defines a relative price. Relative
price is nothing else but the DOW's average price divided by the NYSE's average
price.* The
relative price gives a more realistic description of how DOW moves. It may
reveal, for example, that DOW’s poor performance is not so poor after all, or
that an apparently good performance is not that good.
It is true that DOW's performance and NYSE's performance are strongly
correlated (that's why we use the DOW as an index!) But in a particular day it
may be that the average NYSE stock gains 15%, while the average DOW stock only
3%. In this case DOW's performance must be considered rather poor. In contrast,
if some day the average NYSE stock drops by 5% while the DOW remains unchanged,
the latter's performance should be considered as rather good.
Large-capitalization stocks present
more resistance to the whims of the market (small-capitalization stocks are
know to be more "fickle"). We can therefore use the relative price as
a barometer for detecting exaggerated market moves, be it in the direction of
overstating or understating. This is a dynamic detection process, i.e., it can
only be done on the move, as things change with time. For example, if DOW's
price increases between two dates more than the DOW's relative price between
the same dates, the DOW is overstating the market and we are having a bubble
situation. If DOW's price decreases faster than its relative price, we have an
under-valued market most likely to be followed by a bull market. Large bubbles
can burst with a crash. Following a crash, the total NYSE value generally finds
itself below the real value, and a bull market is likely to follow.
During an overstated market both the
NYSE and the DOW may form bubbles, but the two bubbles do not generally grow at
the same rate. The difference between the percentage change of the DJIA average
price and its relative price is proportional to the size of the bubble.
Therefore a null difference is evidence that there is no bubble.
The bubble
indicator updated
Exhibit 3 shows that the average price and the average relative price of
the 30 industrials moved hand in hand for most of the last 34 years (most of
the points are close to the zero line). Occasionally we see important
excursions upward with price increasing faster than relative price, or downward
with relative price increasing faster. Let us look more closely at some large
excursions in each direction. From the three tallest spikes (bubbles) in 1971,
1975 and 1987 only the last one burst abruptly. An undervalued market preceded
the first two bubbles, which is what may have caused the formation of these
bubbles in the first place. If it is true that a bubble sometimes forms as a
reaction to an undervalued market, it may be reasonable to conclude that such a
bubble is not likely to burst via a crash but rather diffuse via a more gentle
mechanism (soft landing). After all, the amplitude of the 1975 bubble exceeded
that of 1987, and yet it did not burst.
Conversely among the largest market undershoots that we see in
Exhibit 3, only the one in 1987 should be interpreted as a reaction to the
bubble that preceded it. In that light, we can say that the other four market
dips not preceded by bubbles were caused by more deeply seeded phenomena. All
the same, they were followed by bubbles, which can now be seen as reactions to
the dips.
To summarize, a bubble or a dip of the market can be viewed as action or
reaction, depending on whether it initiates a deviation from zero, or follows a
deviation from zero. The relative-price indicator obviously enhances our
ability to predict reactions more than actions.
Let me point out here that over-shoots and undershoots of the market often coincide with bull markets and bear markets respectively. But for the bear markets of 1977 and of spring 1997 there is neither significant overshoot nor undershoot. We must therefore conclude that the poor performance of the DJIA in these two cases was not a correction (i.e. a reaction) but was simply real.
Finally, it must be noted that six-month samples are
not appropriate for slow moving bubble and dips like the bubble leading to the
bear market during 2000-2002. In this case both the up and the down movement
spread over semesters.
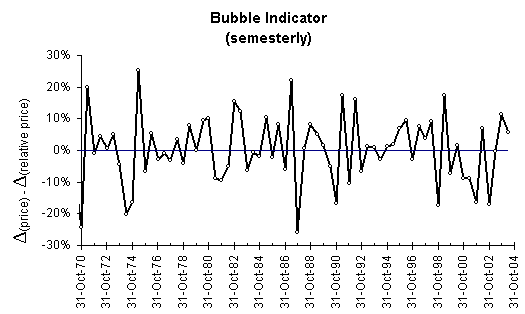
Exhibit 3.
Based on the last 34 years (points every six months), we can say that
bubbles and dips of the market do not extend beyond 25 percentage points in the
difference between the average DJIA price and its relative price. On April 30,
2004 we are in a situation of a mild bubble.
We also see in Exhibit 3
that during late 2003 and early 2004 the market was on the bubble side, which
can be interpreted to some extent as a reaction since undervalued market
preceded it (see Oct-2002).
However, the bubble
indicator on April 30, 2004 was only +5.6% a rather modest value not capable of
triggering a burst. Bubbles burst and dips trigger bull markets when the
amplitude of the indicator excursion approaches 20 percentage points or more.
Exhibit 4 shows a somewhat
different indicator. We see here variable sampling with finer time resolution.
We are looking at daily data to detect a bubble with respect to April
13, 1999. This date was chosen for two reasons. First because it corresponds to
a time when the DJIA was again at a level comparable to today’s, and second
because it also was a time of a mildly overvalued market. We see in Exhibit 4
that following April 1999 the DJIA went undervalued until late 2000 in a rather
smooth non-violent way. A violent dip appeared in the later part of 2001 and
much of that turbulence had non-financial origins. But since then this bubble
indicator edged upwards coming to levels very similar to those of April 13, 1999.
Exhibit 4 demonstrates
better than Exhibit 3 the classic by now bursting of “The bubble” because as we
mentioned earlier six-month sampling is too rapid to describe a process spread
over a whole year.
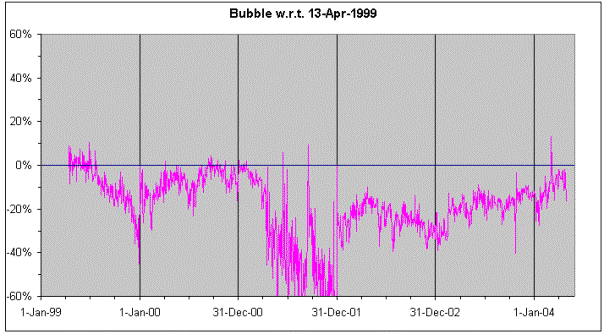
Exhibit 4. Daily data indicate the existence of an
undervalued market with respect to April 13, 1999.
The conclusion is that the market today is slightly overvalued, as it was in April 1999. Barring
external events such as those of 911, we can reasonably expect a non-violent
steady dip ahead of us. Modeling it on the pattern of Exhibit 4 we could
expect it to last until late this year.